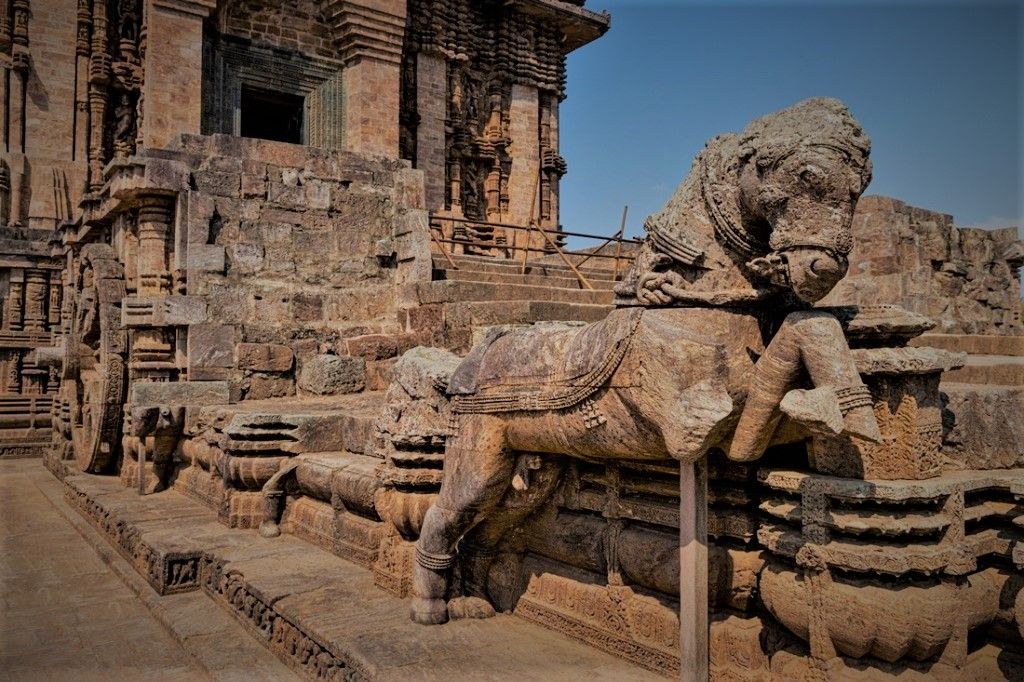
Ancient Universities of India were pioneering institutions that shaped the intellectual landscape of not just the subcontinent but also the world. From the rigorous study of philosophy and medicine to the meticulous development of grammar and mathematics, these centers of learning fostered innovation, debate, and cultural exchange.

While the northern regions of India are renowned for housing world-famous universities like Nalanda, the south too had its own unique scholarly traditions that flourished in temple complexes and monasteries.
In this article, we take a journey through some of the most significant ancient universities of both northern and southern India, showcasing the rich educational heritage of the country.
Northern India: The Rise of Residential Universities
In ancient northern India, several prominent universities attracted scholars from across Asia, laying the groundwork for the country’s intellectual and philosophical advancements. These institutions were well-organized, often residential in nature, and offered a range of subjects, from the sacred Vedas to the rational science of logic.
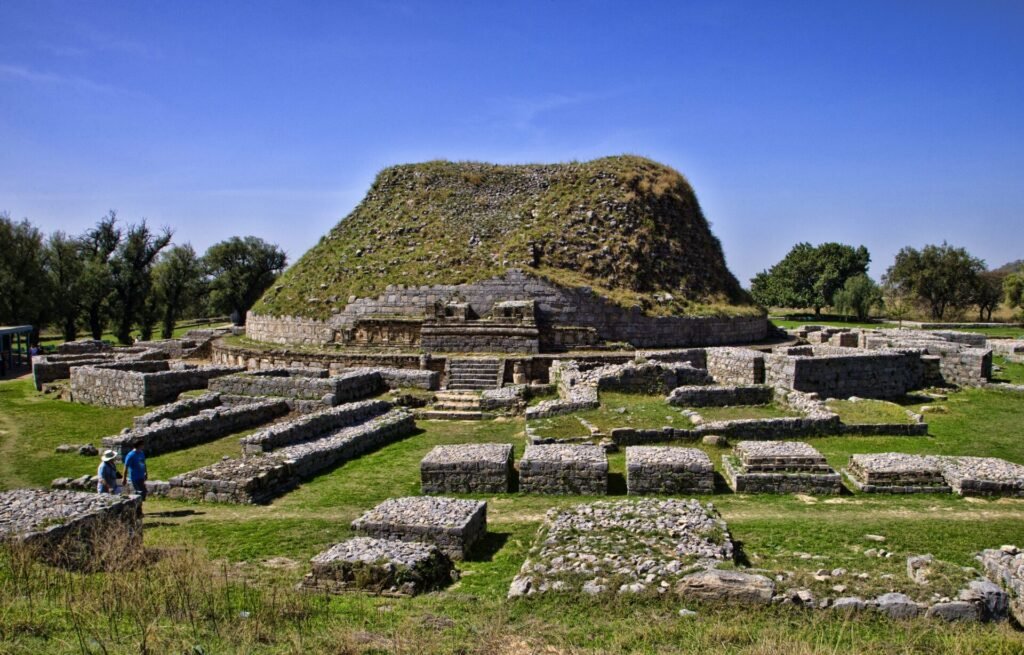
1. Takshashila (Taxila)
- Location: Present-day Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan; historically Takshashila, part of the Gandhara Kingdom
- Period: 6th century BCE to 5th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Vedas, Grammar, Philosophy, Medicine, Mathematics, Astronomy, Logic, Politics, Arts, Warfare
- Famous Scholars: Panini (grammar), Kautilya (author of Arthashastra), Charaka (medicine)
- Legacy: Considered one of the world’s earliest universities, Takshashila was renowned for its multidisciplinary approach and attracted students from as far as China, Greece, and Babylon.

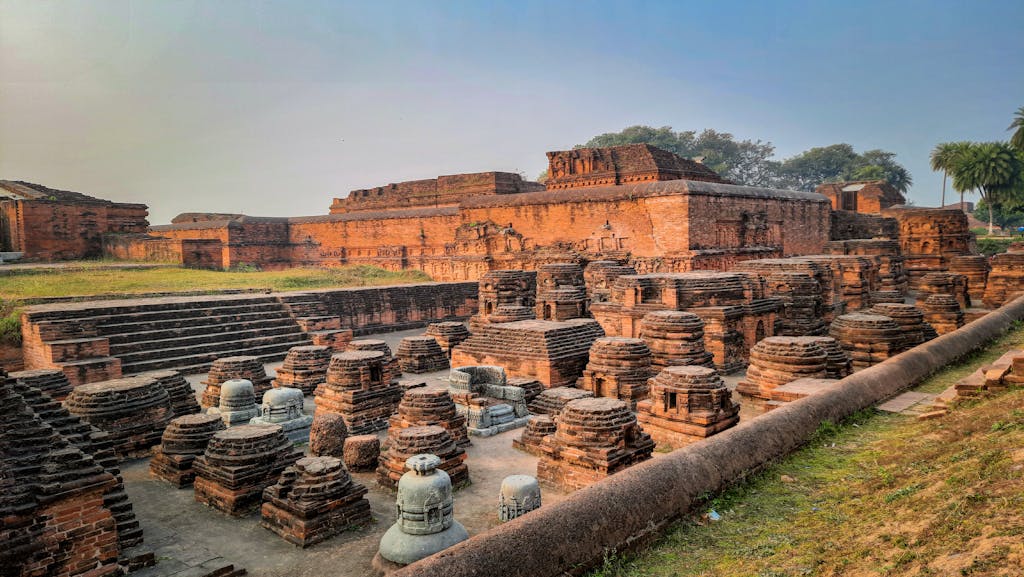
2. Nalanda University
- Location: Present-day Nalanda, Bihar, India; historically Nalanda, under the rule of the Gupta Empire and later the Pala Dynasty
- Period: 5th century CE to 12th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Buddhist Philosophy, Logic, Medicine, Mathematics, Astronomy, Literature
- Famous Scholars: Xuanzang (Chinese traveler), Shantarakshita, Dharmapala
- Legacy: Perhaps the most famous ancient Indian university, Nalanda attracted scholars from all over the world, including Korea, Japan, China, Tibet, and Southeast Asia. Its vast library and residential facilities made it a beacon of knowledge.

3. Vikramashila
- Location: Present-day Bhagalpur, Bihar, India; historically part of the Pala Empire
- Period: 8th century CE to 12th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Buddhist Philosophy, Logic, Tantra, Grammar, Astronomy
- Famous Scholars: Atisha, a key figure in the spread of Buddhism to Tibet
- Legacy: Known for its specialization in Tantric Buddhism, Vikramashila was one of the premier centers of learning under the Pala Empire, often rivaling Nalanda.
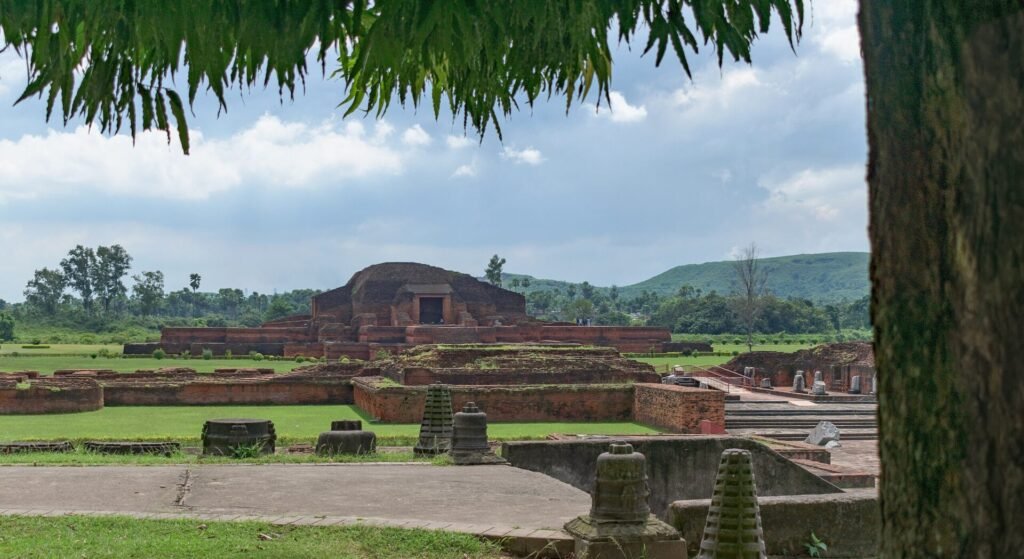

4. Valabhi University
- Location: Present-day Bhavnagar, Gujarat, India; historically Valabhi, capital of the Maitraka Dynasty
- Period: 6th century CE to 12th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Buddhist Philosophy, Law, Political Science, Economics, Medicine
- Legacy: A major center for Buddhist teachings, Valabhi was also known for producing scholars who were well-versed in governance and statecraft.
5. Odantapuri
- Location: Present-day Bihar Sharif, Bihar, India; historically part of the Magadha region, under the Pala Dynasty
- Period: 7th century CE to 12th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Buddhist Philosophy, Logic, Medicine, Literature
- Legacy: Another key center under the Pala dynasty, Odantapuri is believed to have served as a precursor to later Tibetan monastic universities.

6. Jagaddala
- Location: Present-day Naogaon District, Bangladesh; historically part of Bengal, under the Pala Empire
- Period: 11th century CE to 12th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Buddhist Philosophy, Tantra, Grammar, Literature
- Legacy: Known for its scholastic contributions to Buddhist philosophy, Jagaddala was a refuge for scholars fleeing from the destruction of other major universities.

Southern India: Scholarly Pursuits in Temple Complexes and Monasteries
While northern India boasted residential universities, southern India developed educational hubs within temple complexes and monasteries. These centers often blended religious teachings with academic knowledge, fostering intellectual and cultural exchanges.
1. Kanchi (Kanchipuram)
- Location: Present-day Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India; historically Kanchi, capital of the Pallava Dynasty
- Period: Flourished from the 4th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Philosophy, Grammar, Literature, Astronomy, Medicine, Hindu Theology
- Famous Scholars: Bodhidharma (credited with spreading Zen Buddhism to China), Dignaga (Buddhist scholar)
- Legacy: Kanchipuram was a major hub for both Hindu and Buddhist learning, attracting students from across Asia and establishing itself as a critical center for South Indian intellectual life.

2. Ennayiram
- Location: Present-day Ennayiram, Tamil Nadu, India; part of the Chola Kingdom
- Period: 11th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Vedic Studies, Grammar, Logic, Literature
- Legacy: Supported by the Chola kings, Ennayiram was a prestigious Vedic school that hosted hundreds of students and emphasized Vedic traditions and intellectual inquiry.
3. Madurai
- Location: Present-day Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India; historically Madurai, capital of the Pandya Kingdom
- Period: Sangam period (3rd century BCE to 3rd century CE)
- Subjects Taught: Tamil literature, Poetry, Philosophy, Grammar
- Famous Scholars: Thiruvalluvar (author of Thirukkural), Nakkeerar (poet)
- Legacy: Known for its famed Sangam Academies, Madurai was the cultural and literary heart of the Tamil world, where poets and scholars gathered to advance Tamil literature.
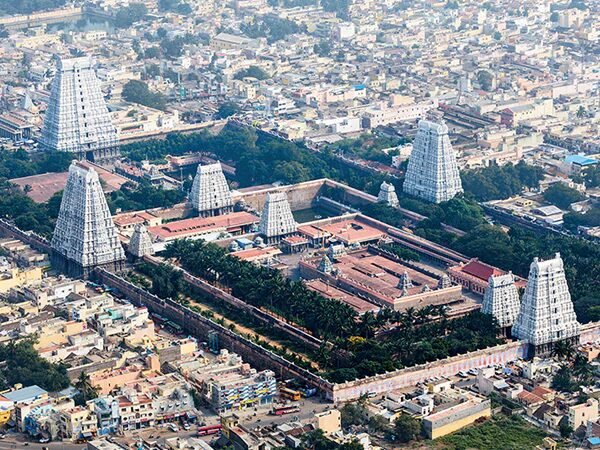

4. Sringeri Sharada Peetham
- Location: Present-day Sringeri, Karnataka, India; historically part of the Chalukya and later Vijayanagara Empires
- Period: Established in the 8th century CE
- Subjects Taught: Vedanta, Hindu Philosophy, Sanskrit, Logic, Mathematics
- Legacy: Founded by Adi Shankaracharya, Sringeri became a preeminent center for Advaita Vedanta and remains one of the most influential educational institutions in India.

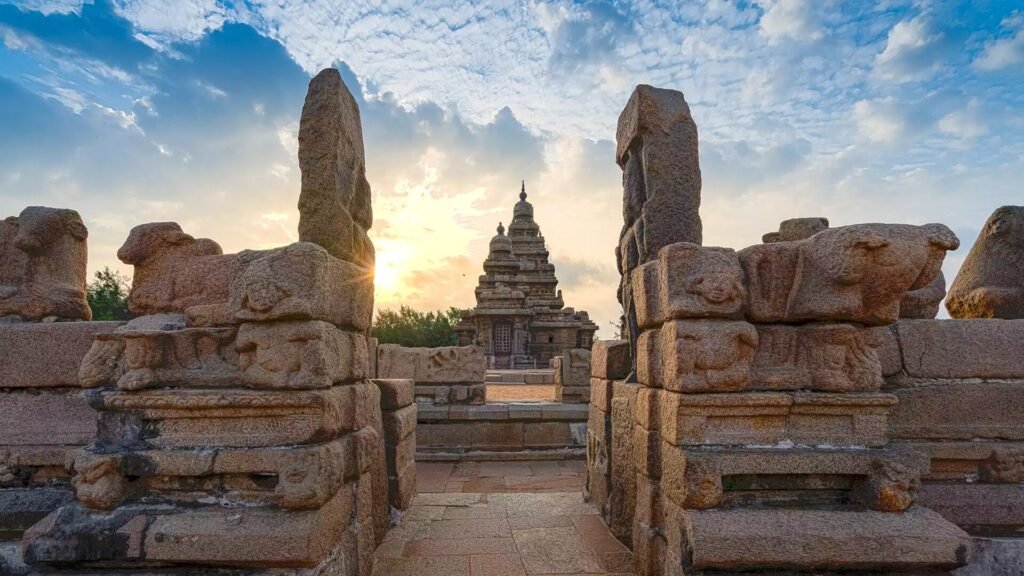
5. Mahabalipuram (Mamallapuram)
- Location: Present-day Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu, India; historically part of the Pallava Dynasty
- Period: 7th century CE onwards
- Subjects Taught: Architecture, Sculpture, Temple Design, Art
- Legacy: Known for its intricate temple architecture, Mahabalipuram was a center where sculptors and builders honed their craft, contributing to the Pallava dynasty’s architectural wonders.

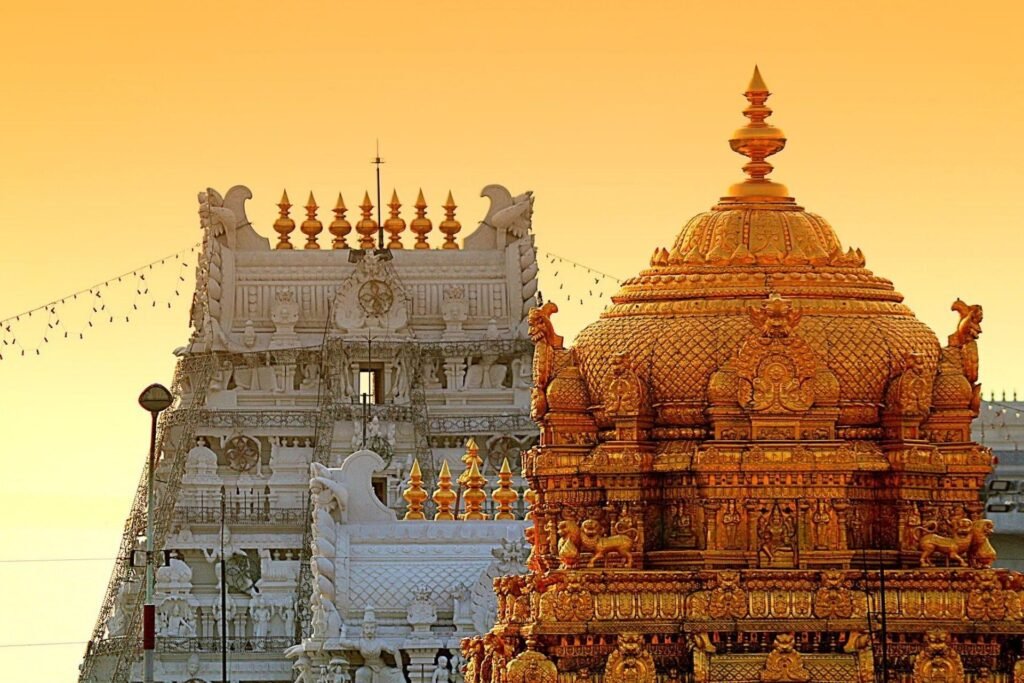
6. Tirupati
- Location: Present-day Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; historically part of the Chola and Vijayanagara Empires
- Period: Medieval period
- Subjects Taught: Vedic Studies, Sanskrit, Philosophy
- Legacy: Though best known for its religious significance, Tirupati also served as an important center for Vedic and Sanskrit learning.

Legacy of Ancient Universities of India
India’s ancient universities were not just centers of education; they were the lifeblood of cultural, philosophical, and scientific advancements that influenced generations. Whether it was the structured, multidisciplinary approach of northern universities like Nalanda or the temple-centered intellectual pursuits in southern India, these institutions laid the foundations for much of India’s intellectual heritage.
Today, these universities remind us of the deep-rooted commitment to knowledge and learning that has shaped the country’s history and continues to inspire modern scholars around the world.