Barsane Wali Holi: The Unique Celebration of Colors
Barsane Wali Holi Holi, the festival of colors, is celebrated with immense enthusiasm across India, but nowhere is it as…
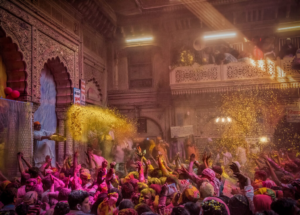
Barsane Wali Holi Holi, the festival of colors, is celebrated with immense enthusiasm across India, but nowhere is it as…

Holi, known as the festival of colors, is one of the most vibrant and joyous festivals celebrated across India and…

Swastika: The Timeless Emblem of Divinity and Auspiciousness The Swastika is one of the oldest and most widespread symbols in…

Tandav, also spelled Tandava, is a powerful and dynamic dance form associated with Lord Shiva, one of the principal deities…

Maha Shivaratri, meaning “The Great Night of Shiva,” is one of the most significant Hindu festivals dedicated to Bhagwan Shiva….

Introduction Sati Mata, also known as Goddess Sati, is a central figure in Hindu mythology, symbolizing devotion, sacrifice, and divine…

Saraswati Mata, revered as the Hindu goddess of wisdom, learning, arts, music, and speech, is one of the most significant…

Hindu mythology is filled with fascinating deities, each symbolizing different cosmic forces and aspects of life. Among them is Goddess…

Shani Dev, also known as Shani Maharaj, is a powerful deity in Hindu mythology, revered as the god of justice…

Meenakshi Temple, Madurai The Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai, Tamil Nadu, is one of India’s most significant and revered temples….

Introduction Lord Shiva, one of the principal deities in Hinduism, holds a significant place in Indian spiritual and philosophical traditions….

1. Hinduism Explained: Origins and Development Indus Valley Civilization Archaeological Evidence and Early Religious Practices The Indus Valley Civilization, one…

Hindu temple architecture stands as one of the most remarkable and enduring facets of Indian culture, evolving over centuries to…

Kartikeya, known by various names like Murugan, Skanda, Subrahmanya, and Shanmukha, is a prominent deity in Hindu mythology. Often depicted…

Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth and last human Guru of Sikhism, stands as a towering figure in Indian history. His…

Introduction The Kumbh Mela is one of the most extraordinary religious gatherings on Earth, where millions of devotees converge to…

In Hinduism, Vayu, the god of wind, holds a vital place in maintaining cosmic order and the rhythm of life….

The Devi Mahatmya is part of a larger Hindu scripture called the Markandeya Purana, written around the 5th to 6th century CE.

The worship of Nagas in India has a deep and enduring legacy, reflecting the rich cultural and religious traditions of the region.

The Ramayana holds an unparalleled place in Indian culture and religion, shaping art, dance, theater, and literature for centuries. Its…
End of content
End of content